The high mortality rate in poultry has always been a nightmare to poultry farmers ab initio. And the major causes of this mortality are as a result of infections caused by several poultry diseases. These poultry diseases affect different parts of the chickens’ body causing the chicken to fall sick and in severe cases death. In the same vine, some diseases only affect some kind of poultry birds, even at a certain age.
Therefore, it is pertinent to understand these diseases, their manifestations, the types of birds they attack, what part they attack, and at what age does it occur for effective management and treatment.
Nevertheless, in this post, I have compiled 12 common diseases of layer chickens, and I have briefly outlined their causes, symptoms, and treatment.
Here are 12 common diseases of a layer you have to watch out for …
Also, read: How To Make Broiler Chicken Grow Faster
1.AVIAN INFLUENZA
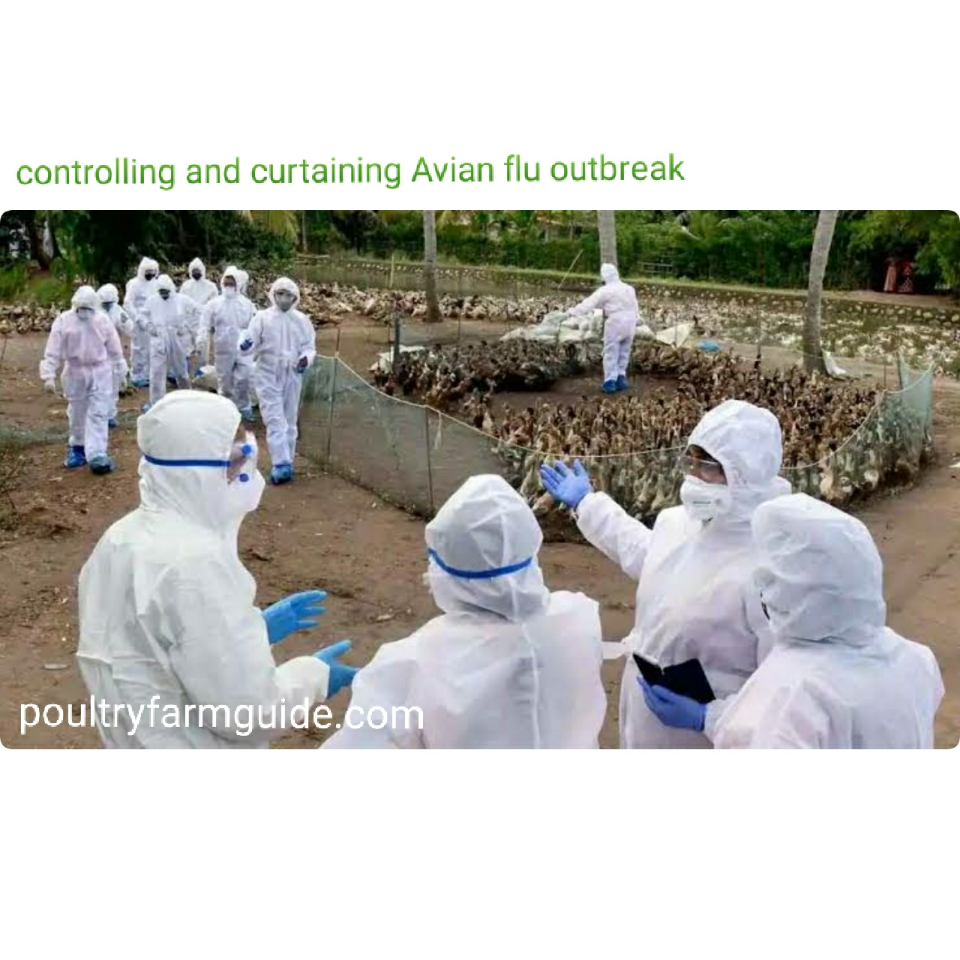

Avian influenza (a respiratory infection) is known informally as avian flu or bird flu. “Bird Flu” refers to an illness caused by any of many different strains of influenza viruses that have adapted to the specific host. Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) is of greatest concern.
Symptoms
- Sudden high mortality
- Decreased feed consumption, excessive thirst
- Respiratory distress (coughing, sneezing)
- Depression and ruffled feathers
- A sudden drop in egg production
Treatment
- Consult your veterinarian immediately
- There is no treatment
- This is a reportable disease and strict biosecurity protocols must be followed
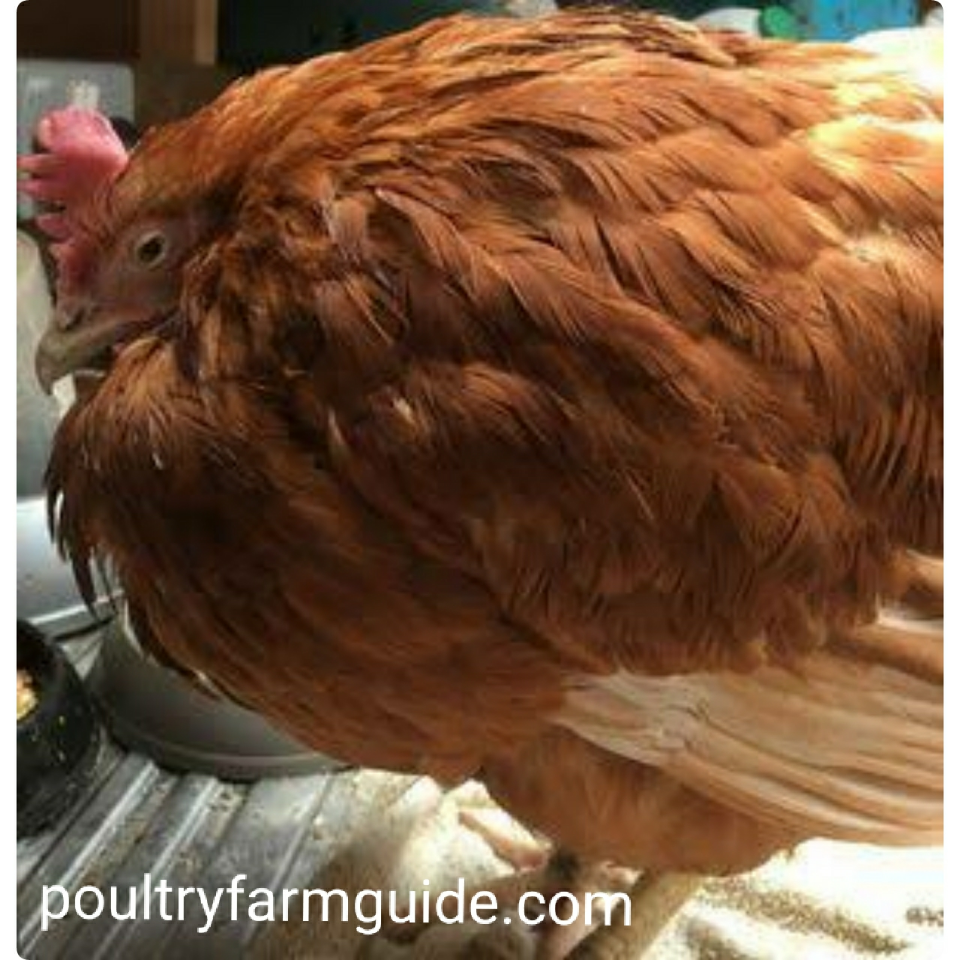
2.CAGE FATIGUE (Calcium Depletion)
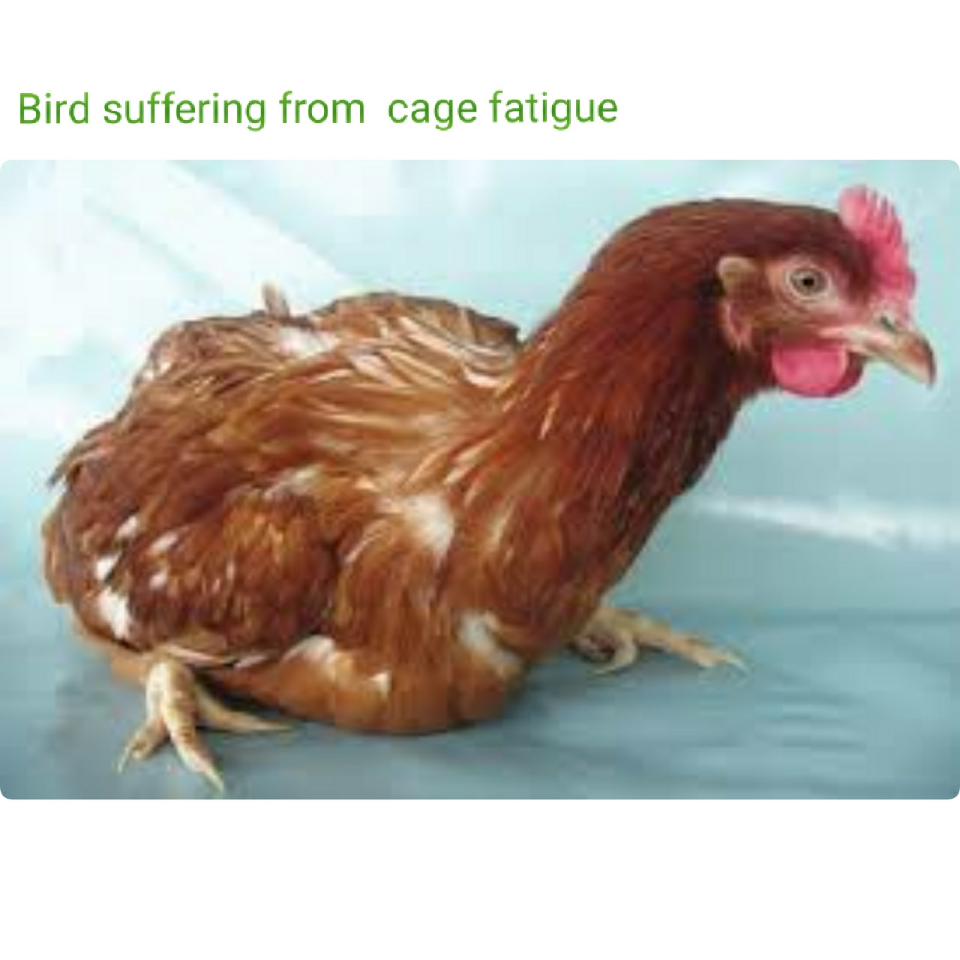

Cage Fatigue results from the depletion of calcium from the bones and starts as soon as egg production begins. Its progress is minimized when birds have the correct balance of calcium, phosphorus, and Vitamin D. High egg production, low feed intake, disease or other stresses can lead to sudden bone loss, especially in less aggressive birds in the flock. Affected hens become unable to stand in the cages and the birds will typically die from dehydration or suffocation when their rib cage collapses.
Symptoms
Increased mortality
- Birds down in cages
- Keel bone soft and pliable
- Drop-in egg production
Treatment
Add Vitamin D3 to the water for 3 - 5 days
- Consult your veterinarian immediately
- Add additional large particle calcium
- Check daily feed consumption (as it often decreases) and adjust the feed density accordingly
- Consider implementing a midnight feeding
- Consider stacked feedings
Also, read: How to Make Chicken Lay Big Eggs and Make More Profit
3.Coccidiosis

Coccidiosis is caused by a unicellular parasite, coccidiosis does not usually affect layers in cages. However, there have been more diagnoses of this problem over the last few years
Symptoms
Mortality increase from 22 to 24 weeks of age
- Mortality often starts in one row or level
- Evidence of bloody droppings
- Egg production can be affected
- Increased mortality
- Birds going out of production, but not showing signs of any sickness
Treatment
Consult your veterinarian immediately. A veterinarian diagnosis is essential as treatment can vary from doing nothing in mild cases to adding products in both feed and water in severe cases.
4.Fatty Liver (Haemorrhagic ) Syndrome
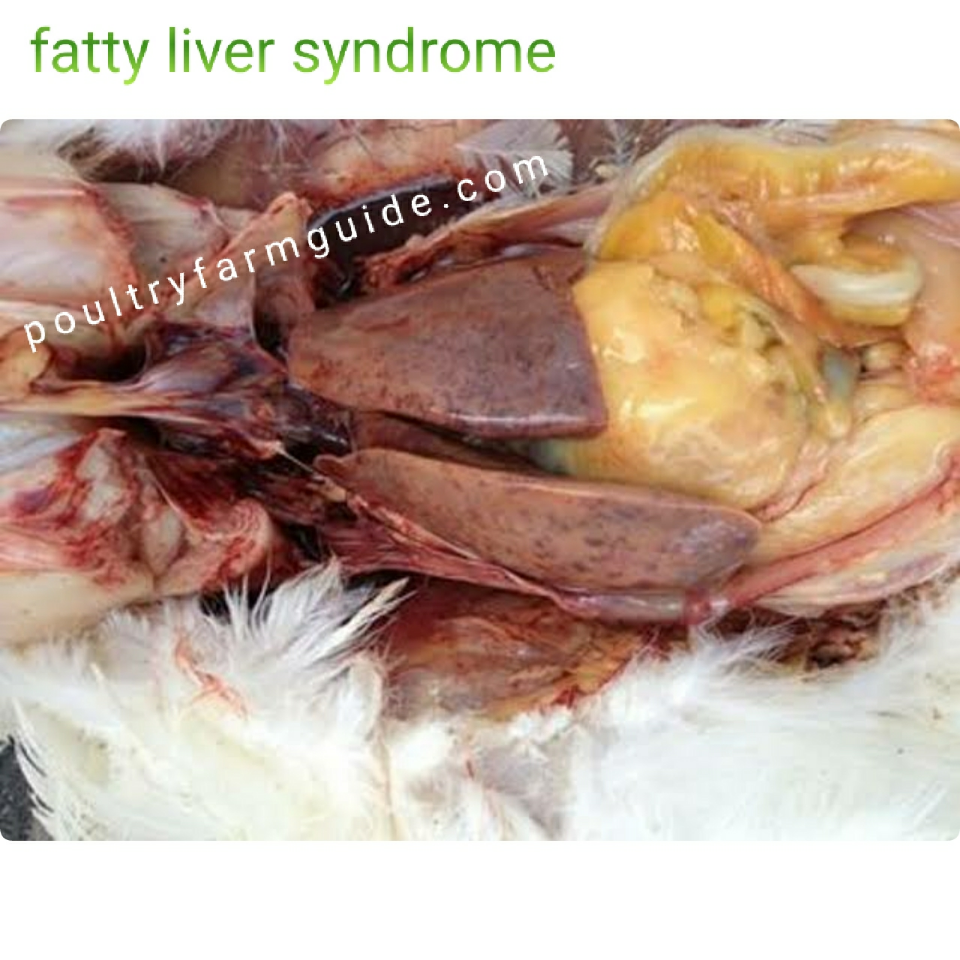
This is a metabolic disease that occurs when excess fat is deposited in the liver of affected hens. This causes the
liver to become soft and more susceptible to damage. Affected die suddenly when the liver ruptures, resulting in massive internal hemorrhage. The dead birds are often larger, healthy birds with high production
Symptoms
Increased mortality
- Birds going out of production, but not showing signs of any sickness
Treatment:
Consult your veterinarian
immediately.
- Add fatty liver pack to feed order for three weeks. This is a diet supplement, and although not always successful, can help birds in some cases.
Also, read 8 Beginner's guide in poultry farming in Nigeria you must follow If you want to be successful
5.Fcal Duodenum (necrosis (FDN))
This intestinal disease typically appears in flocks in early lay, with the only visible sign being the production of smaller eggs. The cause of this disease is not well understood.
Symptoms
- Small eggs
- A slight decrease in production
- Potential failure to peak
- Pale combs
Treatment
Consult your veterinarian immediately
- Extended in-feed administration of antibiotics until production and egg size have returned to normal
6.Infectious Bronchitis
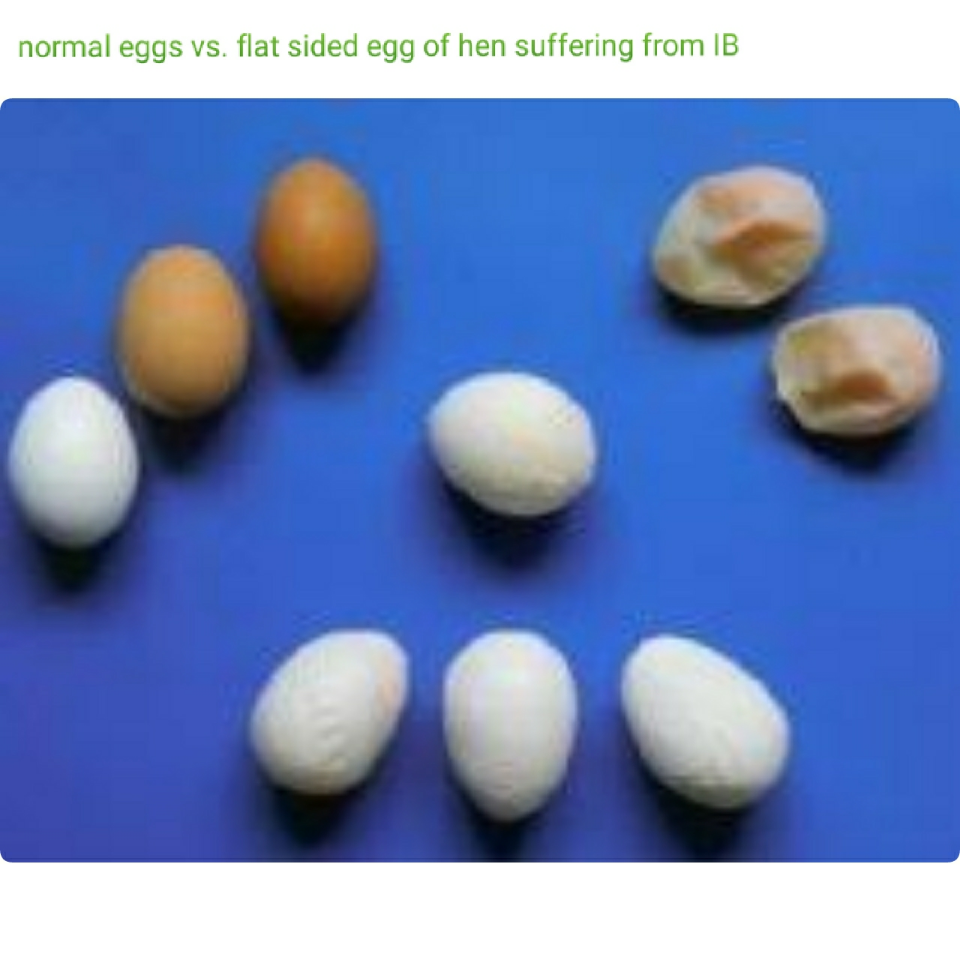

Infectious bronchitis is caused by a virus and is generally well controlled by vaccination during the pullet growing phase. However, the virus is unstable and tends to mutate into new forms against which the vaccines may be less effective. This disease does not typically cause mortality in the flock, however, it can impair growth and do permanent damage to the reproductive organs in the pullet phase and it causes a drastic drop in production in the laying phase.
Symptoms
Sudden rise in mortality, which persists for weeks or months
- Decrease in flock uniformity caused by an inability of affected birds to reach feed and water due to some degree of paralysis
- Delayed feathering
- Flat sided egg
Treatment
Consult your veterinarian immediately
- Take blood samples immediately, as well as 18 - 21 days after that to determine if the flock is recovering
- Adjust calcium intake to coincide with drop-in feed intake
7. Infectious Laryngotracheitis (ILT)
ILT is caused by a virus and most outbreaks are traced back to transmission by contaminated people or equipment. The incubation period varies from 4 to 12 days. Birds are usually vaccinated for ILT with an eye-drop vaccine and control of this disease has been very good.
Symptoms
Respiratory distress, which results from blockage of the trachea
- Depression
- Extreme difficulty breathing, leading to death from suffocation
- Drop-in egg production in laying hens
Treatment
Consult your veterinarian
- Vaccinating the flock as soon as a diagnosis is made may help as this is a slower moving disease
Also read: 8 Natural growth boosters/ promoters for broiler that actually worked
8.Marek Disease

Marek’s Disease is caused by a virus and is usually controlled by vaccination of day-old chicks at the hatchery. Occasional outbreaks occur when the vaccine either fails or is improperly administered, or when a particularly hostile virus infects the flock.
Symptoms
Mortality increase from 22 to
24 weeks of age
- Mortality often starts in one row or level
- Evidence of bloody droppings
- Egg production can be affected
Treatment
Consult your veterinarian immediately as a professional diagnosis must be obtains
- No effective treatment, however steps can be taken to eliminate the virus from the premises before the placement of the next flock
9.Newcastle Disease

ND is caused by a virus and this virus has many strains (mild, medium, and virulent or strong). Transmission is usually from spreading infected manure or nasal discharge, between farms by people or equipment, wild birds, or wind. The incubation period is usually between 3 to 6 days. Birds are usually vaccinated in the pullet barn and control of this disease has been very good.
Symptoms
Respiratory distress (gasping, coughing)
- Decreased feed intake
- Nervous signs, such as twisted necks
- Decreased egg production
Treatment
There is no treatment for ND. Vaccinate your DOC appropriately
Also, read: 10 ways to sell and market your broiler chickens fast that are proven to work
10. Northern Fowl Mite
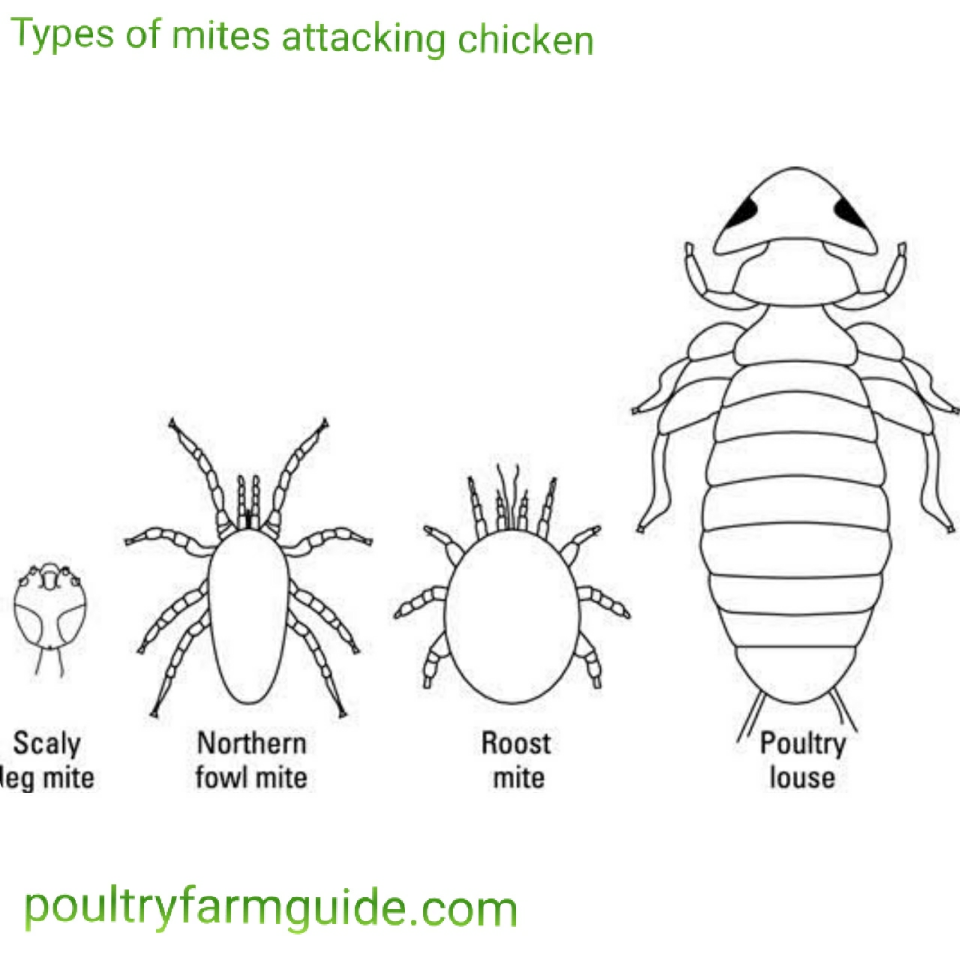
Fowl mites are regarded as the primary and most serious parasite in poultry. They are common on wild birds and rodents. Can lead to a major infestation of commercial poultry operations. The entire life cycle is spent on the host where it feeds on blood and causes major irritations.
Prevention is key and all measures must be taken to ensure no wild birds or rodents can enter the barn and clean up any spilled feed that may attract insects and rodents.
Symptoms
Reduced feed intake
- Weight loss
- Pale comb
- Decreased egg production
Treatment
Consult your veterinarian
- Treatment options are
very limited during the life
of the flock
11.Parasites/ Worms
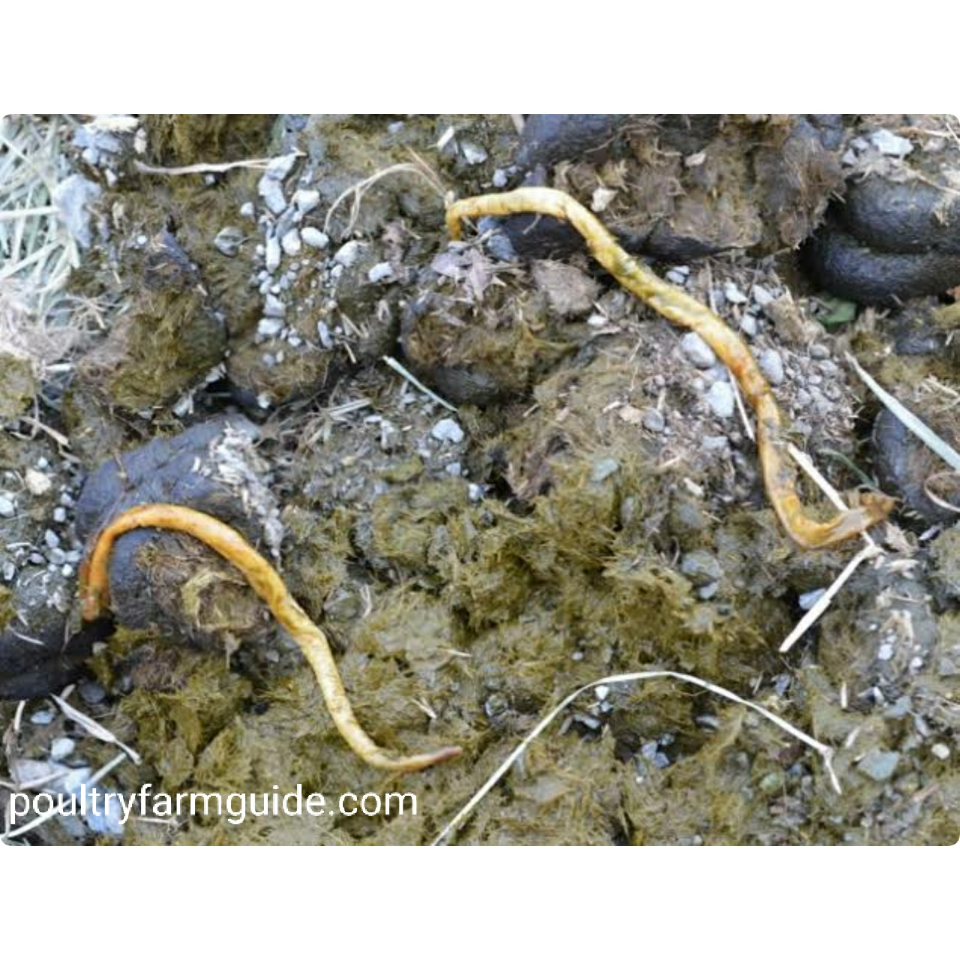

Hens become infected with worms by picking up worm eggs from litter, soil, or droppings. Once infected, worms harm the hen’s intestines. There are three main types of worms found in laying hens
Roundworms: large, very. White and up to 5 cm in length.
Hairworms: Smaller worms. They can cause major damage, even with moderate infestations.
Cecal worms: Fairly harmless worms - can host another parasite called Histomonoas meleagridis (cause of Blackhead Disease)
Symptoms
Decreased shell quality
• Decreased yolk color
• Drop in egg size and production
• Decreased body weight gains
• Stunted or uneven birds
• Increased vent pecking
Treatment
Good sanitation will help control an outbreak
• If hens have access to outside, good drainage and rotation are required.
12. Vent Trauma/ Cannibalism,/ Prolapse
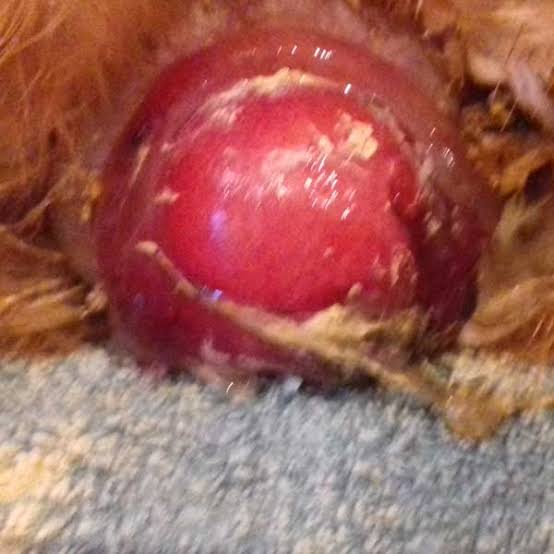
This condition may be caused by over-crowding and high temperature and is often exacerbated by calcium insufficiency.
Symptoms
Increased mortality
- Bloody eggs
- Drop-in production
Treatment
Consult with your veterinarian for possible management solutions if the percentage becomes abnormally high.
- Slowly decrease light intensity or install red sleeves over fluorescent tubes
Reference:
- Simon M. Shame,(2005), Handbook on poultry diseases. Published by: American Soybean Association.
- Pullet and Layer Management Guide by New-Life Mills,2021
Please comment, and share!
Share on Twitter Share on Facebook
Comments
Awwalino 2 years, 11 months ago
Nice one sir. More knowledge to gain from you
Link | ReplySamuel Ezenwankwo 2 years, 11 months ago
Thanks, Awwalino
Link | ReplyNew Comment